There are many types of insects in the environment. For simplicity the main wood destroying insects are referred to here. These fall into two basic groups. “Beetles” and “Termites”.
Wood Destroying Beetles
These live in almost all climates so are widely distributed across the world. An adult female beetle lays her eggs in the fine cracks of a suitable wood substrate. Eggs laid on unprotected wood surfaces hatch and larvae emerge to burrow into wood. The larvae may spend anything between 1 to 5 years inside the wood causing extensive damage. It is in the larval stage that the destruction of the wood occurs. Finally the larvae pupate and form into adult beetles which emerge from the wood leaving characteristic holes. The adults reproduce then the female seeks out suitable wood to lays her eggs on and the cycle is repeated.
Impra Coatings are an excellent physical barrier against female adults laying their eggs on a wood surface and Impra Wood preservatives make the timber unpalatable to the larvae and stop their progress and growth.
There are 6 main types of wood destroying beetles, of widely varying size and distribution.
Woodworm
“Woodworm” is the name commonly used for beetles from the Anobium family. The common furniture beetle is a small beetle of around 3 - 4 mm long. Their larvae feed on starchy wood so tend to prefer sapwood to heartwood, however they will feed on any timber and are a serious commercial pest. The larval stage lasts from 3 to 5 years so it is not uncommon for an infestation to go unnoticed until serious damage has occurred. Infestation can sometimes be detected if a fine wood flour called “frass” is seen, or by the give-away flight holes of 1mm diameter where an adult has emerged from the wood.
The Death Watch Beetle is a similar but larger beetle at around 7mm long renowned for infesting historic buildings. The adult makes a tapping or clicking sound at night to attract a mate which gives it its name.
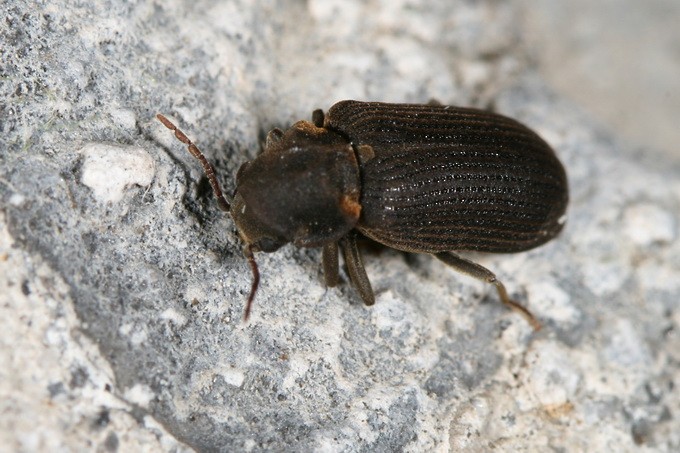


House Longhorn Beetles
The Hylotrupes is the main commercial pest. It is a large beetle with a life cycle of 2 – 10 years. The adult leaves an oval exit hole of 6 – 10 mm diameter in the surface of the wood. Where it occurs the damage this beetle causes is extensive.
Powder Post Beetles
As the name suggests the larvae of these beetles live primarily outdoors and are often responsible for reducing posts and other outdoor wooden structures to powder. They live predominantly in hardwoods.
Ambrosia Beetles
Ambrosia beetles are unusual as it is the adults, not the larvae which bore into wood. The tunnels they form are used to house the larvae and to cultivate a fungus which the larvae eat as food. This process also infects sound wood with fungus and other pests.
Termites
Termites are social insects living in a colony comprising a number of breeding males called kings and one or more breeding females called queens. The rest of the colony is made up of workers and soldiers. A colony may range in numbers from a few thousand to several million.
There are 3 main types of wood destroying termite,
Subterranean Termites live below ground in damp conditions. These live exclusively in darkness and forage for dead plant material which includes wood. They build enclosed shelter tunnels to protect themselves as they travel from the nest in search of food. These shelter tunnels are typically hidden below ground however termite tunnels will cross exposed surfaces and they may be visible above ground in some circumstances.
Dry-wood Termites live in wood which can be at a moisture content as low as 5%. For this reason they are a serious threat to timber in buildings where the dry environment might lead to the expectation the wood is protected.
Damp-wood Termites live in damp wood, which is often partially decayed. These tend to be less of a commercial problem since the wood they infest is often already damaged by other agents.
Irrespective of which type of termite all will voraciously consume wood without exposing themselves to the surface, so no visible indication of their activity is likely until the wood has been eaten away to the point that the structure collapses.
Termites thrive in warm conditions so their natural habitat is in tropical and temperate latitudes where frost is rare. In more recent times however termite colonies have spread to the foundations of large cities in much colder climates where frost does not reach.
Where termites of any kind occur, damage to wooden structures can be formidable and protection against them is essential.
Impra wood preservatives are essential in regions where termites are known or even suspected of being active.

Other Wood Boring Insects
There are numerous other insects which will bore into wood, including carpenter ants, wood wasps, and others, however the damage these insects cause unlikely to be structural and will be is far less serious than the truly wood destroying insects. They do have commercial importance however as they are the main reason for biosecurity issues when transporting wood around the world.
Impra Wood Preservatives meet biosecurity requirements for wood used for packaging and other global transport purposes.